Apple Patent Explains What Makes the HomePod So Special
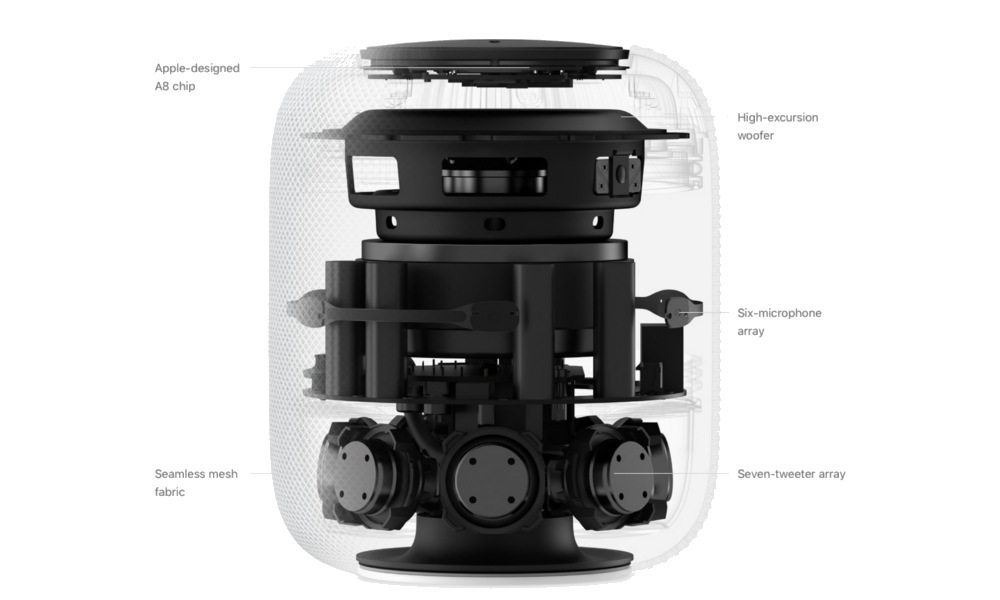

Image via Apple
Toggle Dark Mode
Apple stunned spectators at WWDC 2017 last month by introducing a bevy of new hardware products, including new Mac computers, new iPad Pro models, and perhaps most interesting of all, the company’s first-ever, standalone Siri speaker, which has been dubbed HomePod. While Apple executives spent plenty of time outlining the HomePod’s key specifications and real-world applications, however, very little about the $349 device’s capabilities and underlying technology is known at this time. Fortunately, an Apple patent that was filed back in January of 2016, and published by the U.S. Patent & Trademark Office (USPTO) Thursday morning, might help us to connect some of the dots and in the process prove what a mighty, powerful, and technologically advanced speaker Apple has in store for this holiday season and beyond.
Apple’s “Loudspeaker Equalizer” patent, No. 20170195790, outlines a technology called “smart awareness,” which draws upon a variety of high-tech, smartphone-caliber components to help the device intelligently adapt to its imminent environment. Among these powerful HomePod components include an A8 SoC as a the central processor, a total of six microphones, seven tweeters, a dedicated, 4-inch subwoofer, and this so-called “spatial awareness” technology as the driving force behind what makes the HomePod truly shine amidst the rising sea of voice-driven virtual assistant offerings.
What Is Spatial Awareness?
Spatial awareness, as defined by Apple, is an invention that seeks to help solve one of the biggest problems with the current slate of wireless speakers on the market: sound variability, or the disparity in sound output as the direct result of where, in relation to the listener, the speaker is placed within a room. If you were to place a wireless speaker, for example, with the main subwoofer output butting-up against the wall, then you’d likely notice a significant amount of muddled and distorted acoustic output as the result of said power radiating right into the wall.
“The position of the listener’s ears with respect to room boundaries will [also] affect the perceived frequency response in a similar manner,” Apple writes.
Apple’s solution to this problem is what gives the HomePod a true leg-up over its rivals, including the Google Home and Amazon Echo. By incorporating a total of six, active microphones around the inside and outside of the unit, Apple’s A8 CPU is able to help equalize and filter sound based on a number of variables including speaker displacement, internal and external pressure levels, and data collected by the HomePod’s hexagonal microphone array.
It’s by comparing these internal and external microphone readings that Apple’s device would then be able to “equalize and dynamically alter sound” based on where the speaker is placed. In contrast to other, less-expensive virtual assistant speakers, the technology outlined in Apple’s patent is capable of intelligently and continuously adapting in real-time — rather than being calibrated every time.
The result? Remarkable audio output with advanced adaptation capabilities, which, as Apple boldly attested, will “reinvent the way we enjoy music.”






