Apple Warns Every iPhone Owner to Never Do This
 MR / Adobe Stock
MR / Adobe Stock
Toggle Dark Mode
The internet is an indispensable resource. However, we also know it can pose potentially significant security and privacy risks.
Understanding the basics of surfing the web and what makes a website secure or not will help improve your overall online security and protect your personal information, like credit card details.
A website is considered nonsecure if it lacks HTTPS (Hyper Text Transfer Protocol Secure) in its URL (Uniform Resource Locator). Basically, a URL is a domain name. The HTTPS standard ensures that all communications between your browser and the website are encrypted, protecting any information you share.
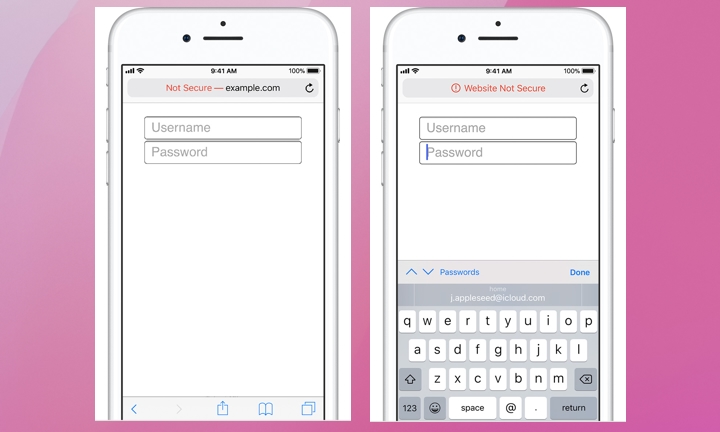
Websites not using HTTPS, as indicated by a plain HTTP in their URLs, pose a risk that the data exchanged can be intercepted by hackers. An example would be https://example.com vs http://example.com.
Risks of Using Nonsecure Websites
Nonsecured websites are low-hanging fruit for cybercriminals. Hackers can intercept data you enter, such as credit card numbers, passwords, or social security numbers, especially if you’re using a public Wi-Fi network.
While using a VPN can help protect you by encrypting everything that leaves your computer, it shouldn’t be considered a foolproof solution. Your traffic still has to come out of the VPN before it reaches the other site, so it can still be intercepted on the other end.
Since it’s relatively easy to add HTTPS security to any website, nonsecure sites often have other potentially serious security flaws, making them easy targets for hackers and other bad actors. That makes them more likely to be used as conduits to deliver malicious software programs, like viruses and malware, onto your iPhone. Once installed, the consequences of those can range from corrupting files to taking over your entire system.
Nonsecured websites are also commonly used for phishing attacks. These sites can mimic a legitimate website, tricking you into providing personal information that’s then used for fraudulent activity or resold on the dark web.
Fortunately, for Apple iPhone users using Safari, Apple warns you when you visit a nonsecure website. If you visit such a site, Safari will display a “Not Secure” or “Website Not Secure” warning. According to Apple, this message indicates any of the following:
- The website is encrypted, but its certificate is expired or illegitimate.
- The website’s certificate is valid, but it uses a much older version of the TLS (Transport Layer Security) encryption protocol that’s no longer considered secure (specifically, TLS version 1.1 or earlier).
- The website is unencrypted and asks you to enter a password or credit card information.
Safely surfing the web requires understanding these security basics. Never enter any personal information or download anything from a nonsecure site. Learning the basics and keeping your app and iOS updates up to date should provide a solid foundation for safe searching. These simple steps will help you significantly reduce the likelihood of falling victim to online threats.