Don’t Get Caught Believing These 12 Common Internet Speed Myths
 Monoliza / Shutterstock
Monoliza / Shutterstock
Internet technology can be a little complex. Most people don’t really worry about the mechanics; they just know when their internet is running too slow. But when trying to speed your internet up, it’s important to know what works and what doesn’t. Continue reading to browse the biggest myths about internet speed, why they’re wrong, and how things really work.
Today’s Internet Connections Are Fiber-Optic
Fiber-optic connections are discussed a lot, but while they may be one of the fastest internet cable options, not everything has been replaced by fiber optic cable. Far from it! America’s internet infrastructure is a hodgepodge of different connection types and different cable types, all trying to work together.
Upgrading to something like fiber-optic cable can take time and money, which is why ISPs (internet service providers) tend to roll out such upgrades slowly, focusing on large cities where many users are. Ultimately, your internet data packets will probably pass through all kinds of connections before reaching their destination. Fiber cable from end to end isn’t guaranteed nor even likely, even when ISPs advertise their super-fast fiber-optic connections.
The More Users Online, the Slower the Internet
This is a simplification that distracts from real issues of internet quality. More people online can create internet slowdowns, but this doesn’t have to happen, and with well-built internet infrastructure, it’s usually not a problem. But how local internet infrastructure manages spikes in traffic can vary significantly across the United States. Some networks won’t have a problem, some will have only minor issues, and some will have horrible performance if traffic spikes above a certain level.
Again, a lot of this depends on local activity and specific servers, not how many internet users are online around the entire country. The internet is designed to be as flexible as possible on the whole: A great example is the jump in internet activity from COVID-19 lockdowns. Internet activity rose significantly (by around 20%) and stayed there for months, but most users didn’t notice a slowdown during this time.
Inside your house, the rules are a bit different – the more users that are on a single connection can make a big difference, because of the limited bandwidth you have - but modern multi-band routers with smart allocation can help address these problems.
Clearing My Cache Will Fix Internet Speed Problems
Clearing your cache is such a common piece of advice that some people think it can solve everything. But remember, your browser cache contains cookies and files that usually work to help webpages load faster. If you clear the cache, you’ll probably slow down your web page load times for a while. Clearing the cache can
work to fix certain bugs and problems with specific website loading, but it’s not going to improve internet speeds overall.
The Closer You Are to Servers, the Better Your Internet Speed
Server
proximity is a factor in internet speeds, but it’s only one factor, and it may
be a very minor one. The problem is that “distance” is very different for the
Internet than it is in the physical world. The last mile of internet
infrastructure before your house could be very poor, and you’ll have internet
speed problems even if you are right by a server.
Congestion is
also important. You can have great server proximity, but if congestion is bad somewhere
along your connection then you will still get data traffic jams and experience
slowdowns and poor ping performance.
My Computer Doesn’t Have Anything to Do with Internet Speeds
Technically, your computer doesn’t affect internet speeds, but it has a huge impact on apparent speed. Remember, every bit of data that your internet delivers has to be processed by your computer. The power of your CPU and GPU has a direct impact on how webpage information appears on your computer, especially with today’s content-rich internet environment. An old, out-of-date computer will be slower as an endpoint. New devices can really make a big difference.
My Slow Internet Is Caused by ISPs Throttling Me
This is a common complaint, but just because ISPs are an easy scapegoat does not mean they are always at fault. First, there’s no guarantee that ISPs are slowing down your internet data, when it could be one of the problems we discussed previously (ISPs have incentives to boost internet speeds when possible, it’s good for marketing).
Second, even if your ISP has guidelines for throttling internet speeds or applying caps that create slowdowns, that doesn’t mean they are always using them in your area, for your connection.
Third, ISPs are not the only ones that can throttle internet data. Another infamous example is government regulations (such as China’s mandatory firewall) that can have similar effects.
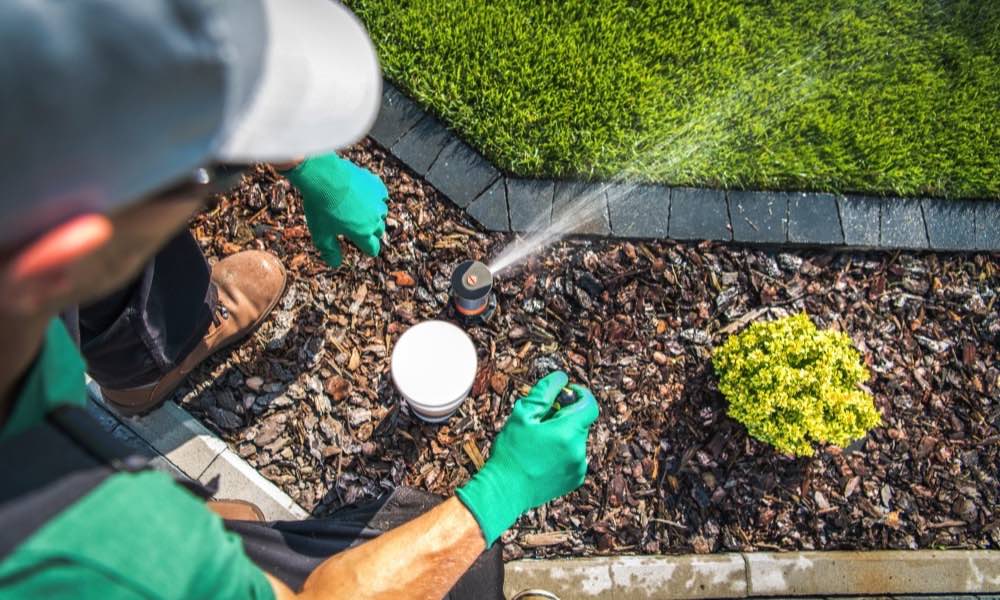
Your Wi-Fi Connection Is Like a Tether Connecting You to a Network
It’s a nice
visual, but not accurate. In truth your router is more like a sprinkler in the
middle of a lawn, spraying packets of data around all the connected devices in
your house. One packet of data to one device, one packet of data to the next,
and so on. This is why adding more devices to a Wi-Fi network can easily slow
it down. Newer router technologies, like MU-MIMO with
Wi-Fi 6, can create lasting connections with mobile devices, but only a few
at a time.
Speed Boosting Software Can Improve Internet Speeds
Speed boosting software has always been a scam. It didn’t make much sense in the dial-up days, and it certainly doesn’t make any sense now. You might as well try to download some extra RAM off the internet. However, cleanup and data management tools like CCleaner may make a small difference in apparent speeds on your computer – plus, they aren’t a scam.
Encryption and Security Slow Down the Internet
This isn’t
usually a problem, especially for at-home encryption and firewalls. While they
may sometimes cause connection difficulties for certain apps, the amount they slow
your actual internet speeds down is negligible. Never try to sacrifice security
for internet speed without consulting with an IT expert first.
Uploading Is Naturally Much Slower than Downloading
It’s actually possible to create internet connections that prioritize upload speeds and vastly improve uploading data. However, since downloading is generally more important for the average user, ISPs and internet infrastructure is designed to cap your upload speed.
Weather Can Slow Down My Wireless Connection
Unless you are using satellite internet, the weather doesn’t have an impact on your internet speeds. For wireless data connections, most cell towers use modern equipment that’s relatively unaffected by harsh weather conditions. Other interference in the radio frequencies data connections use is far more likely to cause problems than any weather event.
A New Router or Modem Can Increase My Internet Speed
There’s a good chance that a new router could increase your apparent internet speeds through new types of connections, faster data processing, better data compression, and lots of other techniques. These are all very cool improvements, but they aren’t actually affecting your internet speeds, just how well internet data is processed once it enters your home.